Introduction
History of BMC
Administrative Structure
Officials of BMC
Departments of BMC
Contact & Complaints
Introduction – The civic body governing the large population of Mumbai city is the BrihanMumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC). It is also known as Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai (MCGM) responsible for providing all civic amenities and had an annual budget of Rs 39039 Crore for 2021-22. The richest corporation in India.
History of Municipal Corporation of Bombay.
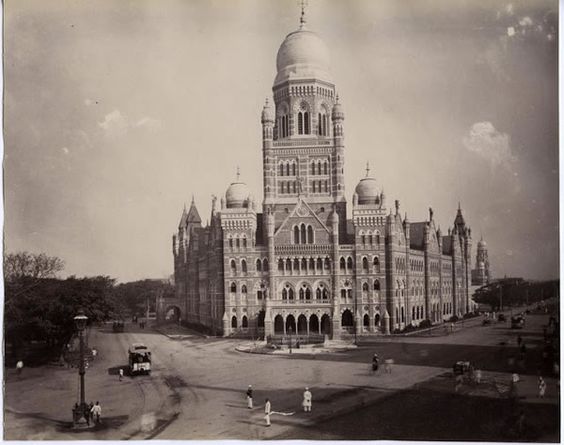
The BMC was formed in 1865 and was headed by Commissioner Arthur Crawford (Crawford Market was named after him). The headquarters which is located near CST railway station was built in the year 1893. The architecture of the building is of the Indo-Sarcenic style, with Gargoyle sculpture in the Neo-Gothic style.
1805 – Municipal administration was formed but in an unorganized way.
1845 – A board of Conservancy of 7 members was formed to manage the municipal funds.
1858 – Three Municipal Commissioners were appointed to improve sanitary conditions. But they were inefficient.
1865 – Governor Sir Battle Frere appointed a new Municipal commissioner Sir Arthur Crawford. He brought positive changes in Mumbai.
1873 – The first municipal elections were held and a total of 64 members were in administration. All 64 were ratepayers of Bombay.
1887 = The new Municipal bill was introduced in the Legislative Council.
1888 – The act of 1888 led to better administration by providing proper responsibilities to its representatives.
1922 – Rate payers were replaced by rent payers and the strength of Corporators was increased to 106 members.
1928 – four more seats were added to trade Unions and in 1950 increased to 135.
1952 – it became a fully elected body. The strength of the Corporation increased from 140 in 1966 to 170 members in 1985.
Pherozshah Mehta played a key role in drafting the Act of 1888. Under this act three main authorities were formed:
The Corporation members
The Standing Committee
The Municipal Commissioner
Administrative Structure:
The city is divided is into six zones and further divided into 24 wards for administrative convenience.
- An Assistant Commissioner heads each ward.
- Further, the Corporation appoints Heads of Departments of the numerous departments that work with a specific mandate such as Water, Health, and Sanitation.
- The Corporation is represented by Corporators elected from that ward. They in turn elect the Mayor of Mumbai who is the first citizen of the city.
- The Corporators form the legislative arm of the corporation.
Officials of BMC
Municipal Commissioner –
The head of the corporation is the Commissioner and is a member of the Indian Administrative Service.
Additional Commissioners
Under the Municipal Commissioner, there are four additional commissioners
Deputy Commissioners –
Under Additional Commissioners there are Deputy Commissioners who are heads of departments such as Solid Waste Management (SWM), Sanitation, Water, Health etc.
Corporators:
In BMC Elections the corporators of political parties are elected for 24 wards which constitutes 237 sub wards. Corporators form the legislative arm of the corporation.
What Corporators do?
- Corporators act as facilitators between citizens and the BMC.
- They oversee BMC’s functioning exercise control over budgetary and financial proposals and lay down policies.
- In effect, they are responsible for the upkeep of the city.
Mayor of Mumbai:
The Mayor is appointed by the elected Corporators who is the first citizen of the city. The mayor is the head of the house, who is usually from the party that got majority seats in the election.
- The mayor’s post is a ceremonial one.
- Elected from among the corporators for a 2.5-year term.
- He is Invited to functions concerning the city and receives visiting dignitaries.
- Chairs general body meeting of all corporators
Departments
Disaster Management – In 1999, the Disaster Management Unit (DMU) was set up at the Municipal Head Office. It was established to tackle disasters in Mumbai. After the deluge in July 2005, it was upgraded with modern equipment to handle emergencies effectively. It works round the clock throughout the year.
The function is to give alerts to citizens and arrange search rescue operations and supply of food during any emergency. Encourage preparedness at all levels.
Disaster Management Unit & CCRS Department
Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai
Basement, Annex Building,
Mahapalika Marg, C.S.T. Mumbai 400001
Tel: +91 22 22694725 / 27
Health: Responsible for issuance of licenses to all entities engaged in production/storage of commodities. Eateries, restaurants, and hotels are also issued licenses by this department. Registration of births and deaths, licenses to private nursing homes.
License Department – The License Department is an administrative department of MCGM and issues licenses in consultation with advice from other technical advisory departments like, Fire Brigade, Health, Engineering, Estate, etc. Given this, the Establishment must obtain a necessary license from the License department before starting manufacturing, storage or trade of any commodity/activity.
Building and Factory: – This department issues various Permits in consultation with and advice from other technical advisory departments like, Fire Brigade, Engineering, Estate, etc. In view of this any Establishment/Individual/Societies must obtain the required Permit from the Building & Factories department before starting any activities
Maintenance Department – The Maintenance Department issues various Permits in consultation with and advice from other technical advisory departments like, Fire Brigade, Engineering, Estate, etc. Permission including Religious Permission, Social Permission, Political Permission, Election Permission, Shooting Permission, Pay & Park, Drainage Connection
Market Department – The Market Department is an administrative department of MCGM which is primarily responsible for supervising and controlling the working and functioning of Markets established and developed by Municipal Corporation. Additionally, it governs the functioning of outside Meat Shops and Cold Storages and controls the activities of import and slaughter of animals/ fowls and sale of contraband meat.
Sewerage Department: It operates and maintains the sewage collection, conveyance, pumping, treatment and disposal system brought in place by the Sewerage Projects and Mumbai Sewage Disposal Projects departments.
Shops and Establishment: Want to set up a shop? You would need to register with this department.
Garden and Trees: One needs to take permission from this department to trim a branch of your neighbouring tree. They regulate the city’s tree cover and grant permission to hold meetings of varied natures (religious, social etc.) on open spaces and municipal gardens.
Water Works: The pipe water supply is one of the earliest civic services provided by the Hydraulic Engineer Department, one of the oldest departments. The main objective of the Hydraulic Engineer department is to operate, maintain and provide water and related services to the citizens of Mumbai.
Solid Waste Management SWM – The SWM Department is headed by the Chief Engineer [SWM] Conservancy, Operation, Planning and Transport Sections of S.W.M. It is responsible for managing around 9000 tons of water generated daily.
Contact and Complaints
Now most of the procedure is made online through e-governance. One can track their applications online.
Citizens can lodge complaints on the number 1916 or by filling up an online form. They can also visit a Citizen Facilitation Centre at 24 wards.
Click here for Online Complaints
Control Room:
Helpline: 108, 022-22269472, 022-22694725, 022-22694727, 022-22704403, 022-24114000
Solid Waste Management: 22617993
Water Complaints:
Mahim to Colaba 022-23678109,
Bandra to Dahisar 022-26184173,
Sion to Mulund 022-25153258







[…] BrihanMumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC) presented the budget of Rs 39,038.83 crores for the year 2021-22. Last year the budget was Rs 33,441.00 crores. This means the budget increased by Rs 5,517.81 (16.74%) this year. Due to Covid-19 there is an extra financial burden on BMC. […]
[…] Mumbai there are 24 wards under BrihanMumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC). For the convenience of city administration, wards have been decentralized. Each ward has its own […]
Comments are closed.